from sympy import symbols, integrate
x = symbols('x')
f = x**2 + 1
area = integrate(f, (x, 0, 1))
print(area) # Output: 4/34/3Lecture 21
University of Arizona
INFO 511
Differentiation rules
Constant rule: \(\frac{d}{dx} (c) = 0\)
Power rule: \(\frac{d}{dx} (x^n) = nx^{n-1}\)
Constant multiple rule: \(\frac{d}{dx} [c \cdot f(x)] = c \cdot f'(x)\)
Sum rule: \(\frac{d}{dx} [f(x) + g(x)] = f'(x) + g'(x)\)
Difference rule: \(\frac{d}{dx} [f(x) - g(x)] = f'(x) - g'(x)\)
From last time:
Measures the accumulation of quantities and the area under a curve.
Example: Used to compute the area under probability distribution functions, which is essential in statistics and data analysis.
Symbol: \(\int f(x) dx\)
Practical Application: Calculating Cumulative Distribution Functions (CDFs)
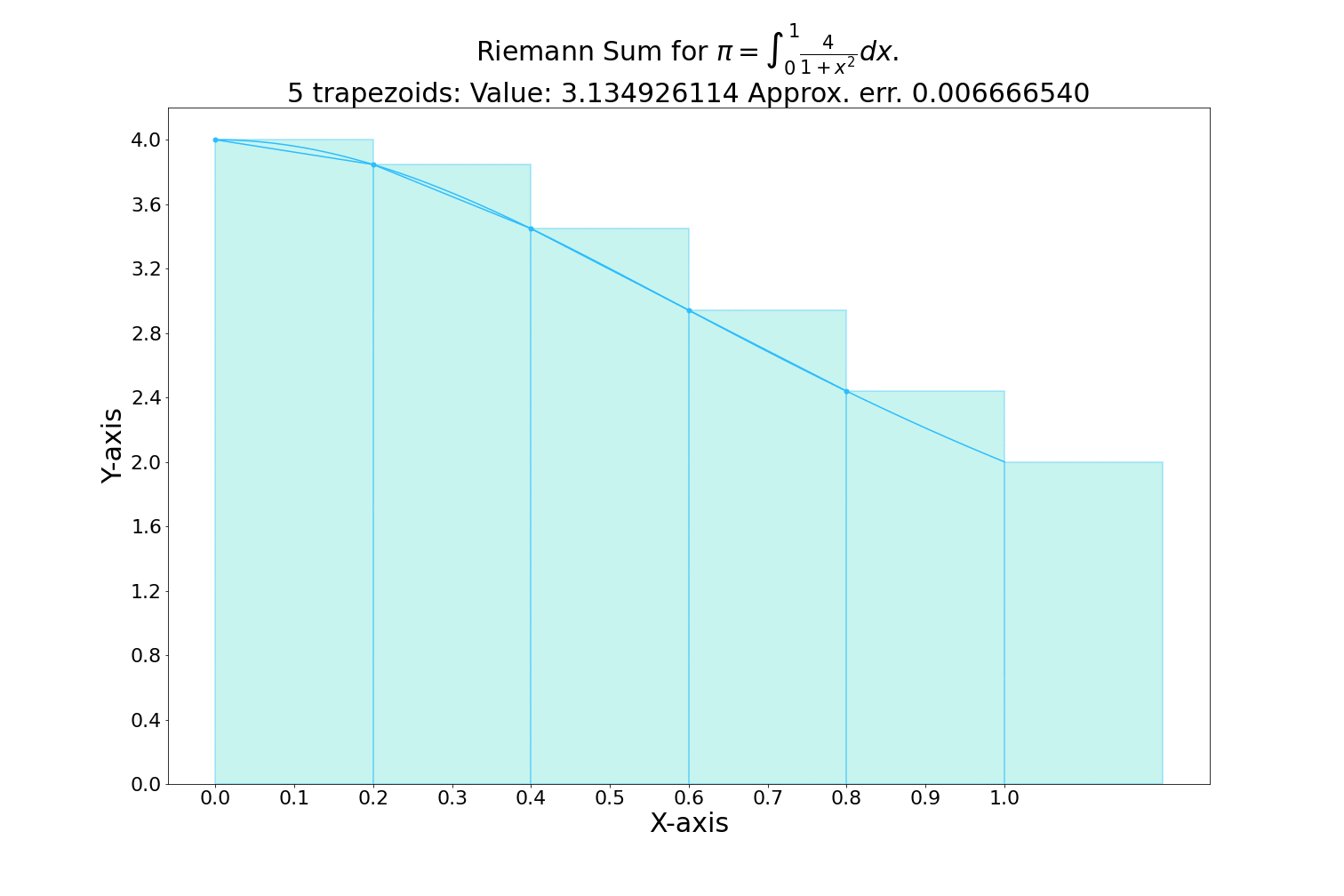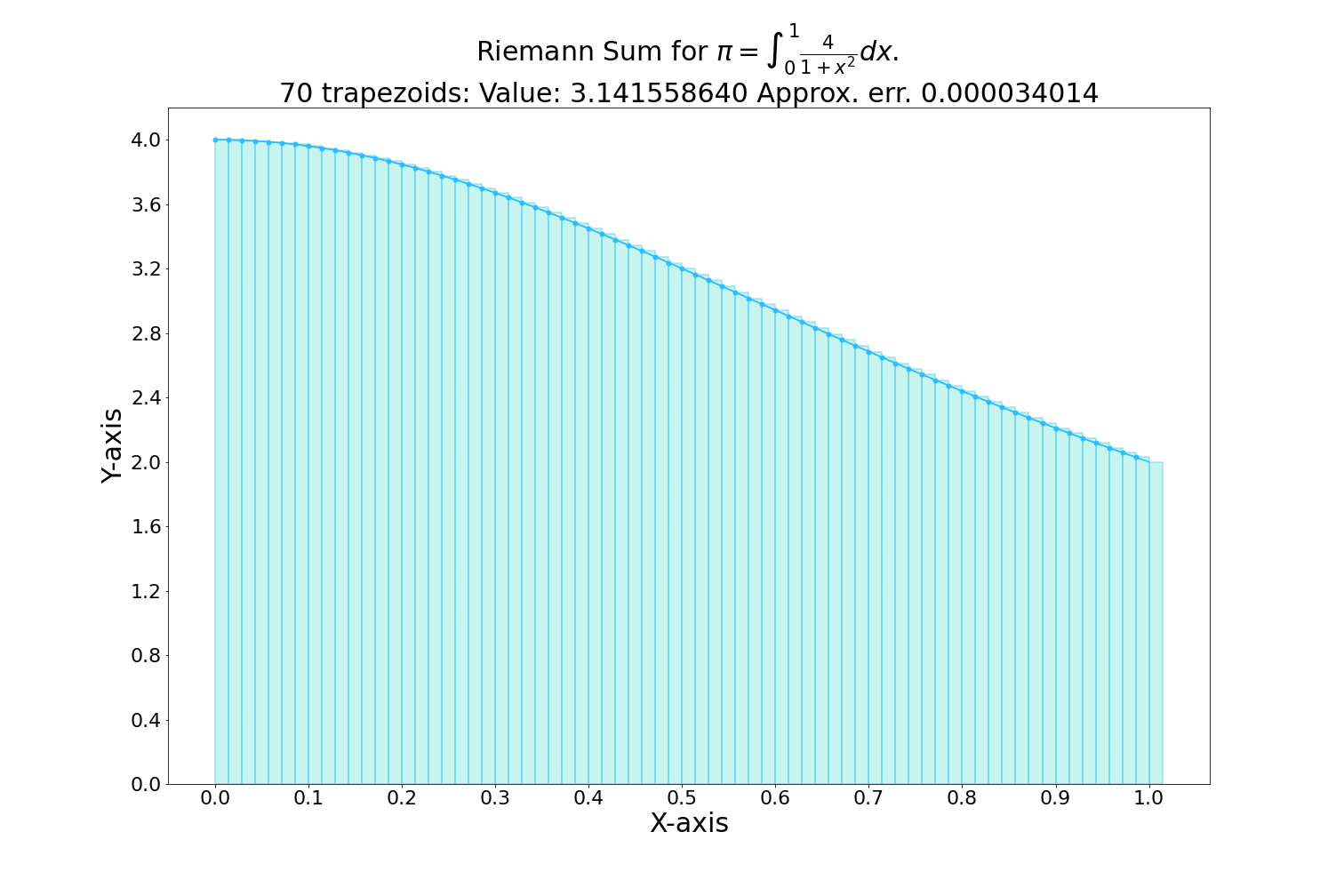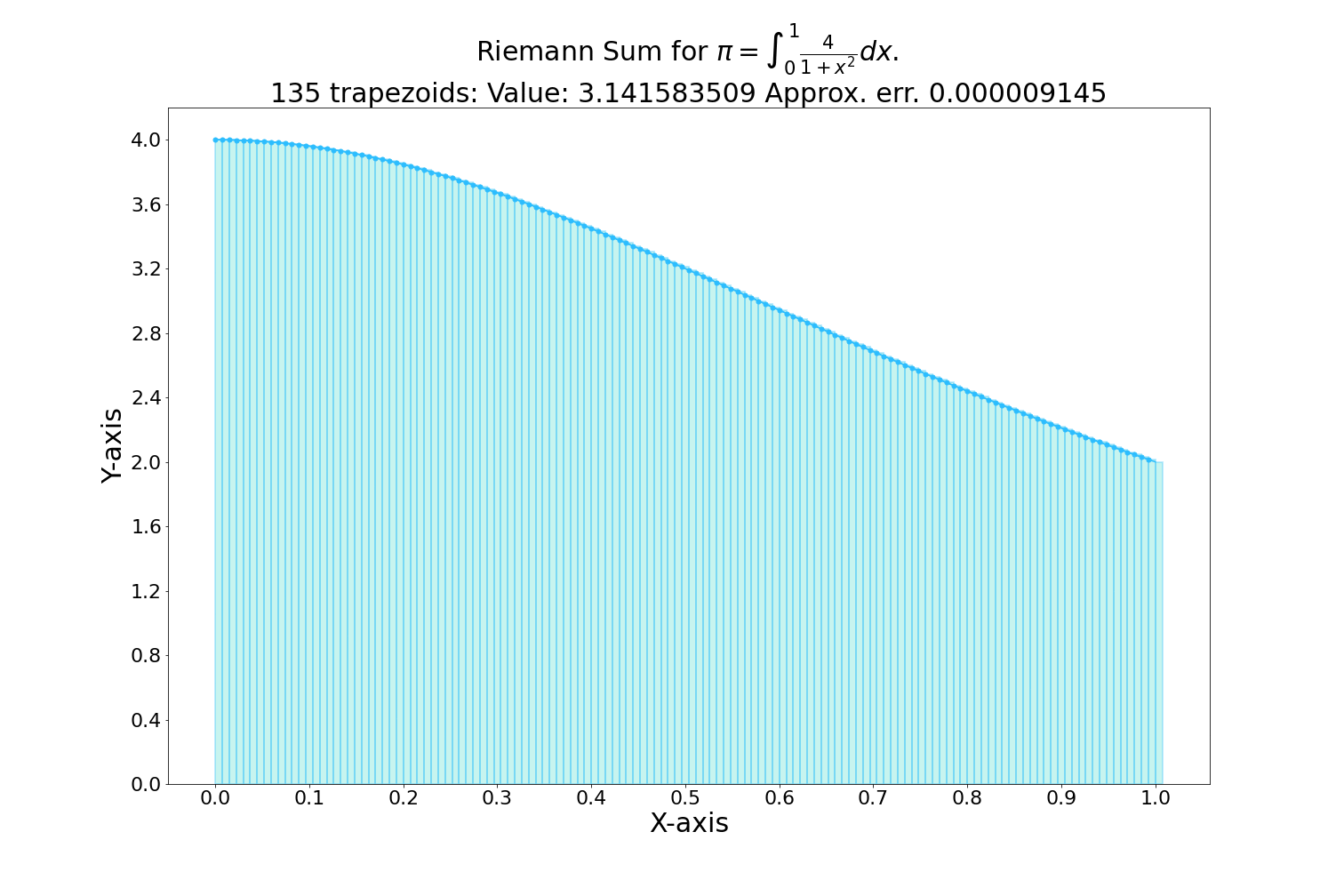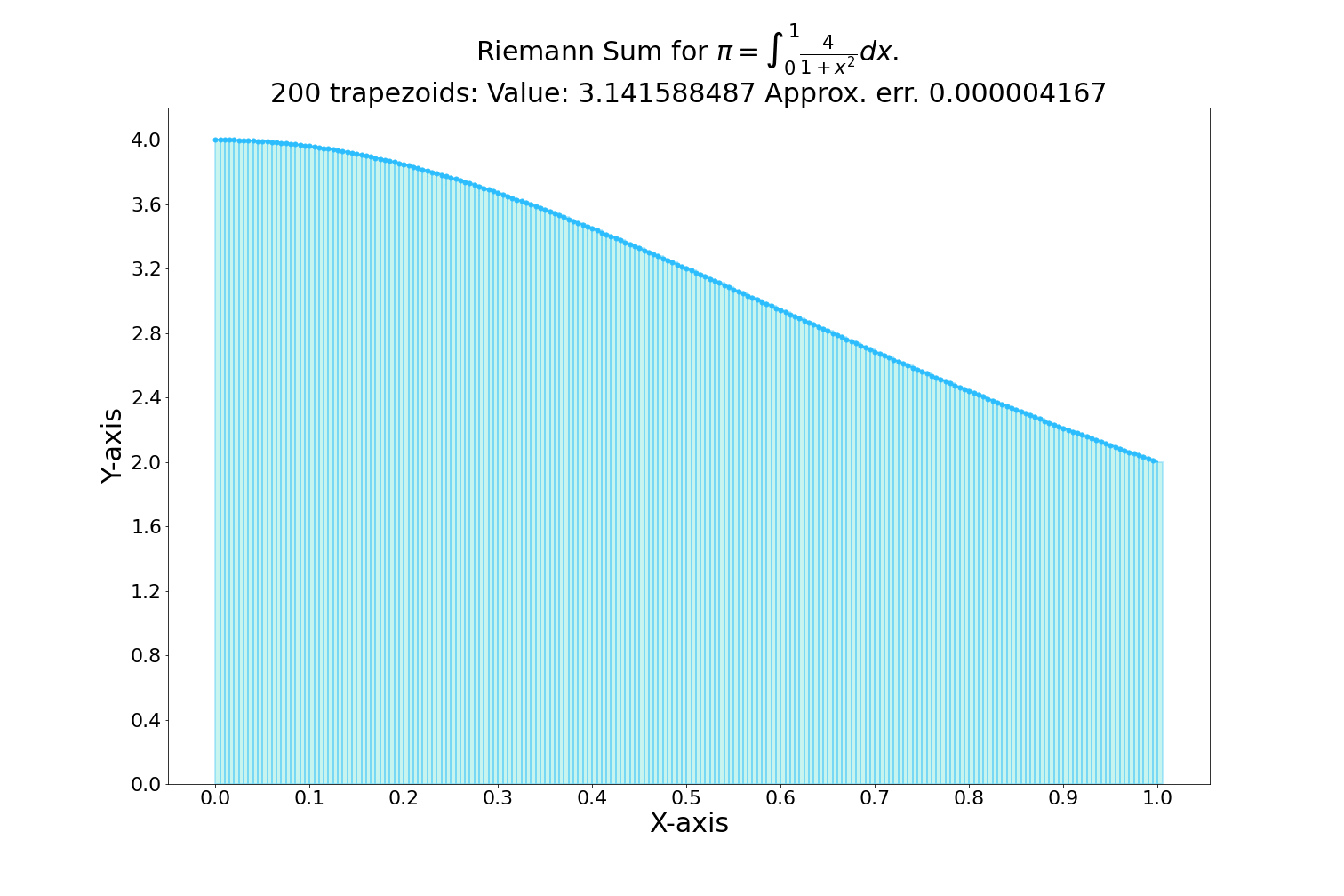
Area under the curve
The integral of a function represents the area under the curve of that function on a graph, between two points.
Example: Finding the total distance traveled given a speed-time graph.
Calculating integrals using SymPy
Integration rules
Constant rule: \(\int c , dx = cx + C\)
Power rule: \(\int x^n , dx = \frac{x^{n+1}}{n+1} + C\)
Constant multiple rule: \(\int c \cdot f(x) , dx = c \cdot \int f(x) , dx\)
Sum rule: \(\int [f(x) + g(x)] , dx = \int f(x) , dx + \int g(x) , dx\)
Difference rule: \(\int [f(x) - g(x)] , dx = \int f(x) , dx - \int g(x) , dx\)
Function: \(f(x) = 7\)
Integral: \(\int 7 , dx = 7x + C\)
Function: \(f(x) = x^3\)
Integral: \(\int x^3 , dx = \frac{x^{4}}{4} + C\)
Function: \(f(x) = 5x^2\)
Integral: \(\int 5x^2 , dx = 5 \cdot \frac{x^{3}}{3} + C = \frac{5x^{3}}{3} + C\)
Function: \(f(x) = x^3 + 4x - 5\)
Integral: \(\int (x^3 + 4x - 5) , dx = \frac{x^{4}}{4} + 2x^2 - 5x + C\)
Complex Integrals:
Involves functions composed of multiple simpler functions.
Requires application of rules like integration by parts and substitution for integration.
Example Function:
\[ \int_{a}^{b} \left( e^{cx} + \frac{1}{x^n} \right) \, dx \]
\[ \int u \space dv = uv - \int v \space du \]
Function: \(\int x e^x , dx\)
\(u = x \quad \Rightarrow \quad du = dx\)
\(dv = e^x , dx \quad \Rightarrow \quad v = e^x\)
\(\int xe^x \space dx=xe^x-\int e^x \space dx=xe^x-e^x + C\)
Function: \(\int xe^x \space dx\)
Differentiate: \(u\colon du=dx\)
Integrate: \(dv\colon v = e^x\)
Function: \(\int xe^x \space dx\)
\[ \int u \space dv = uv - \int v \space du \]
\[ \int x e^x \, dx = x e^x - \int e^x \, dx \]
Function: \(\int xe^x \space dx\)
\[ \int x e^x \, dx = x e^x - e^x + C \]
\[ \int x e^x \, dx = e^x (x - 1) + C \]
Function: \(\int f(g(x))g^{'}(x)dx=\int f(u)\space du\)
Function: \(\int 2x \sqrt{x^2 + 1} , dx\)
\[ \int 2x \sqrt{x^2 + 1} \space dx=\int \sqrt{u} \space du = \frac{2}{3}(x^2 + 1)^{3/2} + C \]
Function: \[\int x \ln(x) , dx\]
\(u = \ln(x) \quad \Rightarrow \quad du = \frac{1}{x} , dx\)
\(dv = x , dx \quad \Rightarrow \quad v = \frac{x^2}{2}\)
Function: \[\int x \ln(x) , dx\]
\[ \int x \ln(x) , dx = \frac{x^2}{2}\ln(x) - \int \frac{x^2}{2} \cdot \frac{1}{x} \space dx = \frac{x^2}{2} \ln(x) - \frac{1}{2} \int x \space dx \]
\[ = \frac{x^2}{2} \ln(x) - \frac{x^2}{4} + C \]
You’ll learn more about this in INFO 521: Introduction to Machine Learning and/or INFO 523: Data Mining and Discovery
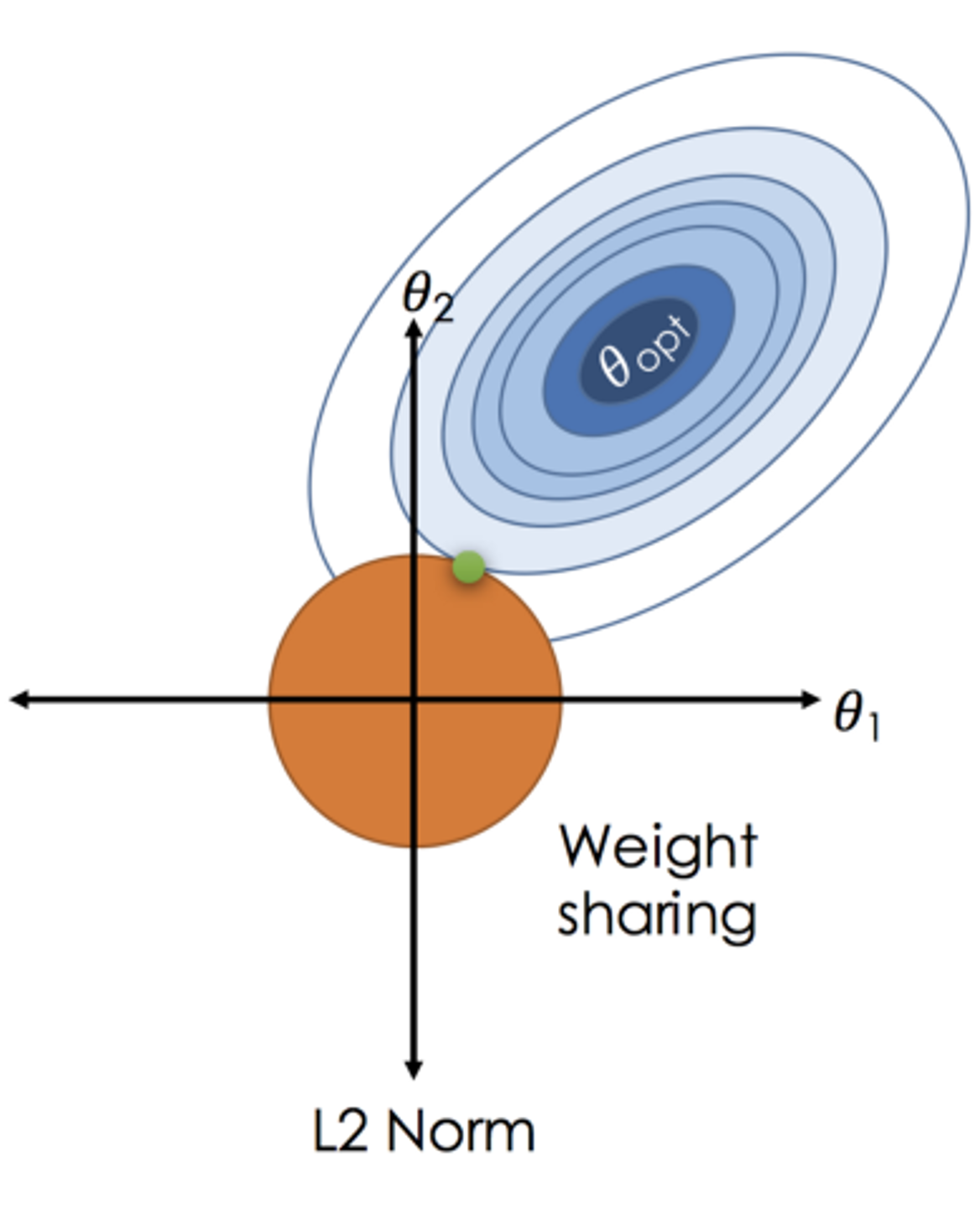
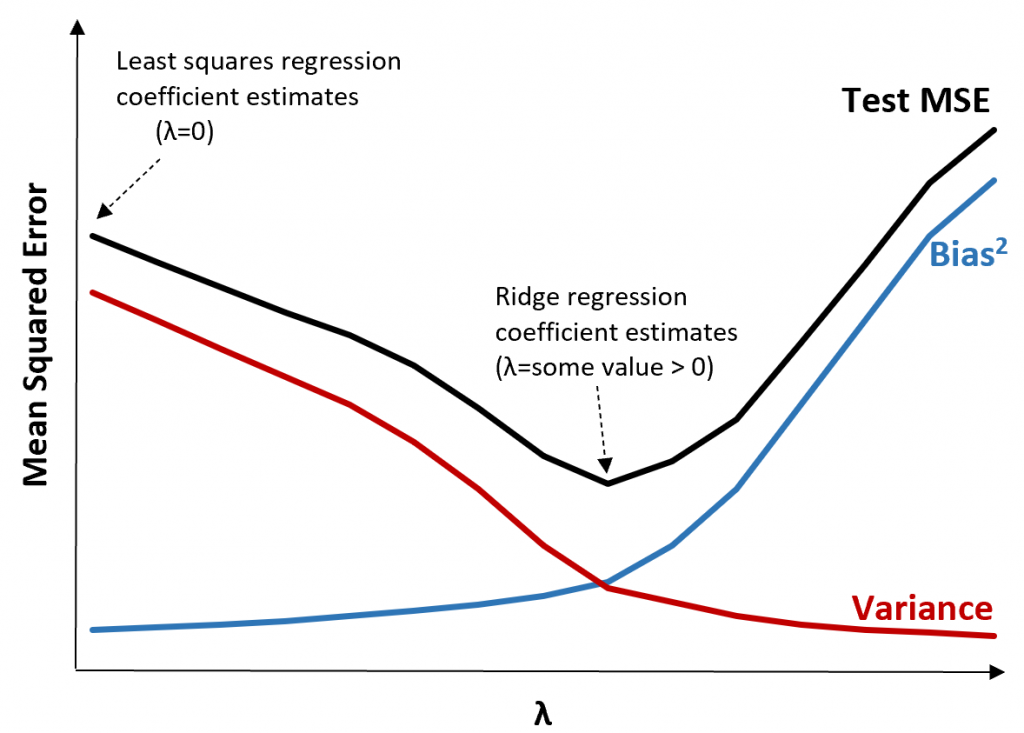
ae-14-integrationPractice integration (you will be tested on this in Exam 2)